Boehringer_Workplace_Lab_Research-01_RGB_010
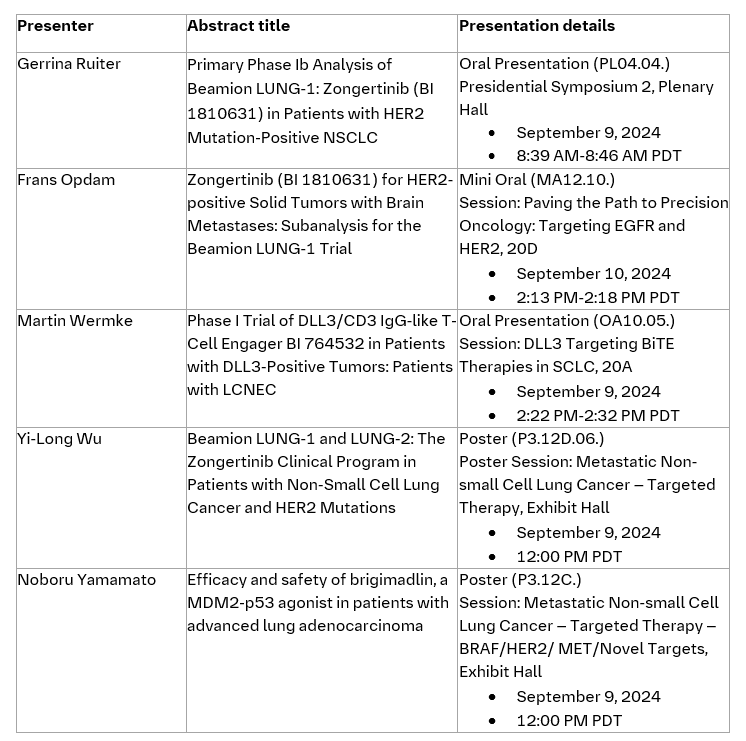
- Data from the phase Ib Beamion LUNG-1 trial selected for late-breaking oral presentation in the Presidential Symposium at WCLC on Monday, September 9.
- The U.S. FDA and China's CDE have granted zongertinib Breakthrough Therapy Designation for patients with HER2-mutated NSCLC and who have received prior systemic therapy.
- Phase I trial data of a novel DLL3-targeting T-Cell Engager, which has already secured FDA Fast Track as well as FDA and EMA Orphan Drug Designations, will also be presented.
At the IASLC 2024 World Conference on Lung Cancer (WCLC) Boehringer Ingelheim will present encouraging data from across its oncology pipeline, illustrating its aspiration to transform the lives of people with cancer by delivering meaningful advances.
Carinne Brouillon, Head of Human Pharma at Boehringer, said: “Every year, about 40,000 people worldwide are diagnosed with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with a HER2 mutation.1 While targeted therapy is available for some cancers driven by HER2, people living with HER2-mutated NSCLC have few options. We are proud to be sharing new data evaluating our investigational zongertinib in this hard-to-treat setting. Our strong oncology pipeline underscores our strategic approach in advancing novel targeted treatments and cancer cell-directed therapies that have a potential to transform lives for generations of patients.”
Late-breaking results from the Beamion LUNG-1 trial, which is a Phase Ia/b trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of zongertinib (BI 1810631), a HER2-specific tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), will be presented at WCLC. This includes new data from a primary analysis of the first Cohort of Phase Ib in pre-treated patients with HER2m+ NSCLC to be presented in a Presidential Symposium on Monday, September 9, from 8:30AM - 10:00AM PDT (Location: Plenary Hall) and featured in the official WCLC Press Program.
Highlighting the potential of zongertinib, the investigational oral therapy was recently granted Breakthrough Therapy Designation by the U.S. FDA and China’s CDE for the treatment of adult patients with advanced, unresectable or metastatic NSCLC whose tumors have activating HER2 mutations, and who have received a prior systemic therapy.
Investigating the potential of DLL3 targeted immunotherapy to transform the treatment of neuroendocrine carcinomas
Exploring the promise of DLL3-targeted immunotherapy in transforming the treatment of neuroendocrine carcinomas, Boehringer will present data from the Phase I trial of its novel DLL3-targeting T-Cell Engager, BI 764532 in an Oral Presentation on Monday, September 9, from 2:22PM-2:32PM PDT (Location: 20A). This investigational treatment, which has been granted FDA Fast Track as well as FDA and EMA Orphan Drug Designations, is currently being evaluated in patients with large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung (LCNEC-L), small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and extrapulmonary neuroendocrine cancer (epNEC). BI 764532 is designed to redirect T-cells to target tumors that express the DLL3 protein.
In addition to the five abstracts to be presented at WCLC, Boehringer will also host a symposium titled "Emerging Therapies in Clinical Practice: What are the Patient Perspectives on the Future of Lung Cancer Treatment?" on Saturday, September 7, from 3:45PM to 4:45PM PDT (Location: 30DE). At Boehringer, cancer care is personal, which is why this event will explore patient viewpoints and expectations regarding the evolving landscape of lung cancer therapy.
Data from Boehringer’s oncology pipeline to be presented at WCLC:
About non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
Lung cancer claims more lives than any other cancer type and the incidence is set to increase to over 3 million cases worldwide by 2040.2 NSCLC is the most common type of lung cancer.3 The condition is often diagnosed at a late stage,4 and fewer than 3 in 10 patients are alive five years after diagnosis.5 People living with advanced NSCLC can experience a detrimental physical, psychological, and emotional impact on their daily lives. There remains a high unmet need for additional treatment options for people living with advanced NSCLC. Around 4.7% of lung cancers are driven by HER2 mutations (or gene alterations).1,6
About zongertinib
Zongertinib (also known as BI 1810631) is an investigational oral HER2-specific tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) that is highly selective and being developed as a potential treatment for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Zongertinib was granted FDA Fast Track Designation in 2023, then in 2024 it was granted Breakthrough Therapy Designation by the U.S. FDA and China CDE for the treatment of adult patients with advanced NSCLC whose tumors have activating HER2 mutations, and who have received a prior systemic therapy. HER2 is a member of the ErbB family of receptor tyrosine kinases (enzymes that act like chemical messengers). Mutations in HER2 can lead to overexpression and overactivation, which can in turn result in uncontrolled cell production, inhibition of cell death and promotion of tumor growth and spread. Read more here.
About BI 764532
BI 764532 is an investigational DLL3/CD3 IgG-like T-Cell Engager under development as a potential new targeted immunotherapy for patients with large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung (LCNEC-L), small cell lung cancer (SCLC) & extrapulmonary neuroendocrine cancer (epNEC). The therapy is designed to directly redirect T-cells, potentially resulting in the selective killing of tumor cells by the body’s own immune system. Pre-clinical in-vivo data suggests administration of DLL3/CD3 bispecific T-cell engager (ITE) monotherapy induces T-cell infiltration into tumor tissues, transforming a non-inflamed (cold) tumor microenvironment into an inflamed (hot) state. This process triggers tumor cell apoptosis, resulting in significant tumor regression. BI 764532 has been granted FDA Fast Track as well as FDA and EMA Orphan Drug Designations. Read more here.
About brigimadlin
Brigimadlin (also known as BI 907828) is an investigational oral MDM2-p53 antagonist being developed as a potential treatment for certain types of cancer. The small molecule compound may inhibit the interaction between MDM2 and p53, restoring p53 wild type function. Inactivation of the tumor suppressor protein p53 is a central mechanism by which cancer cells drive tumor growth. Increased levels of the protein MDM2, a key negative regulator of p53, is a well-characterized inactivation mechanism, seen in about 5-7% of all cancer cases.
About Boehringer Ingelheim in oncology
We have a clear aspiration – to transform the lives of people with cancer by delivering meaningful advances, with the ultimate goal of curing a range of cancers. Boehringer Ingelheim’s generational commitment to driving scientific innovation is reflected by the company’s robust pipeline of cancer cell-directed and immuno-oncology investigational therapies, as well as the smart combination of these approaches. Boehringer’s ambition in oncology is to take a diligent and broad approach, creating a collaborative research network to tap into a diversity of minds, which is vital in addressing some of the most challenging, but potentially most impactful, areas of cancer research. Simply put, for Boehringer Ingelheim, cancer care is personal, today and for generations. Read more here.
About Boehringer Ingelheim
Boehringer Ingelheim is a biopharmaceutical company active in both human and animal health. As one of the industry’s top investors in Research and Development, the company focuses on developing innovative therapies in areas of high unmet medical need. Independent since its foundation in 1885, Boehringer takes a long-term perspective, embedding sustainability along the entire value chain. More than 53,500 employees serve over 130 markets to build a healthier, more sustainable, and equitable tomorrow. Learn more at www.boehringer-ingelheim.com.
References:
1Chia, P. et al. Prevalence and natural history of ALK positive non-small-cell lung cancer and the clinical impact of targeted therapy with ALK inhibitors. Clinical Epidemiology. http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/CLEP.S69718.
2International Agency for Research on Cancer – World Health Organization. Rates of trachea, bronchus and lung cancer. Available at: https://gco.iarc.fr/tomorrow/en (Accessed August 2024).
3Zappa C & Mousa Non-small cell lung cancer: current treatment and future advances, Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2016 Jun; 5(3): 288–300.
4Polanco D et al. Prognostic value of symptoms at lung cancer diagnosis: a three-year observational study. J Thorac Dis 2021;13:1485–1494
5National Cancer Institute Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER). https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/lungb.html (Accessed: August 2024).
6Arcila, M. E. et al. Prevalence, clinicopathologic associations, and molecular spectrum of ERBB2 (HER2) tyrosine kinase mutations in lung adenocarcinomas. Clin. cancer Res. an Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 18, 4910–4918 (2012).
Attachment





