Masimo O3 ® Regional Oximetry Receives FDA Clearance for Somatic Applications and Measurement of Relative Changes in Cerebral Hemoglobin IRVINE, Calif.--( BUSINESS WIRE )-- Masimo (NASDAQ: MASI) today announced that O3 ® Regional Oximetry has received FDA clearance for expanded use in monitoring somatic tissue oxygenation saturation in all patient populations and monitoring relative changes in hemoglobin, oxyhemoglobin, and deoxyhemoglobin in adult brain
Masimo O3® Regional Oximetry Receives FDA Clearance for Somatic Applications and Measurement of Relative Changes in Cerebral Hemoglobin
IRVINE, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)-- Masimo Corporation (NASDAQ: MASI) today announced that O3® Regional Oximetry has received FDA clearance for expanded use in monitoring somatic tissue oxygenation saturation in all patient populations and monitoring relative changes in hemoglobin, oxyhemoglobin, and deoxyhemoglobin in adult brains. With this FDA clearance, O3 is now indicated for use in both cerebral and somatic applications, both in the U.S. and in CE mark countries, for all patient populations.
This press release features multimedia. View the full release here: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20200831005390/en/
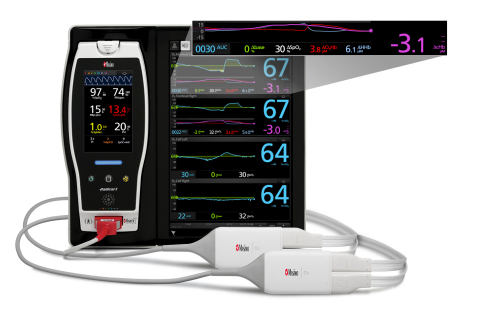
Masimo Root® with O3® Regional Oximetry (Photo: Business Wire)
O3 Regional Oximetry provides regional or tissue hemoglobin oxygen saturation with a trending specification of 3% ARMS* (cerebral and somatic, all ages) and absolute accuracy specifications of 4% ARMS (cerebral, adults) and 5% ARMS (cerebral, pediatric patients) through the use of O3 multi-wavelength sensors and O3 Regional Oximetry near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) technology. Unlike peripheral pulse oximetry, which reflects the body’s general arterial blood oxygenation, O3 provides information about the local tissue’s hemoglobin oxygen saturation, both in cerebral and somatic applications. This information provides additional insight that may help inform clinicians of changes in cerebral or somatic tissue oxygen levels. Monitoring renal tissue oxygenation in neonates has been found to help provide early warning of renal dysfunction.1 Monitoring both brain and somatic tissue oxygenation simultaneously may further improve clinicians’ ability to provide rapid and accurate care.2
André Denault, MD, PhD, Department of Anesthesiology, Critical Care Program at the Montreal Heart Institute and Central Hospital of the University of Montreal, said, “There is a growing interest in the use of somatic NIRS owing to the association of cerebral and somatic desaturation with unfavorable outcomes in shock states. As an addition to O3 cerebral oximetry, the somatic component could serve as an earlier warning of impaired tissue perfusion. Somatic NIRS has been validated as a monitor of peripheral perfusion and shows an excellent correlation with peripheral perfusion compared with radionuclide plethysmography. As previously reported,3 cerebral and somatic NIRS combined with bedside whole-body ultrasound can help in early detection of different types of shock to formulate proper therapeutic strategies.”
Along with FDA clearance for somatic monitoring, the O3 measurements ΔcHb, ΔO2Hb, and ΔHHb are cleared for the monitoring of relative changes in oxygenated hemoglobin (ΔO2Hb), deoxygenated hemoglobin (ΔHHb), and total hemoglobin (ΔcHb) in adult brains. With the expanded indications for ΔcHb, ΔO2Hb, and ΔHHb, clinicians gain information that may provide insight into the dynamic relationship between oxygen and hemoglobin in the brain that brain oxygenation saturation (rSO2) alone may not provide.
Dr. Aamer Ahmed, FRA FESC FACC, Consultant Cardiovascular Anesthesiologist at University Hospitals of Leicester, UK, said, “When using regional oximetry to monitor the brain, rSO2 helps track the oxygenation state of the brain, but understanding the dynamic variations in rSO2 is even more valuable. Changes in rSO2 may be a function of a change in hemoglobin or perfusion, or may result from an oxygen desaturation event. In my practice, I use Masimo O3 ΔcHb, ΔO2Hb, and ΔHHb to gain insight into the relative changes in hemoglobin and perfusion in the brain to help enable earlier detection and intervention during adverse changes to cerebral blood flow.”
O3 seamlessly integrates with Masimo SedLine® brain function monitoring on the Root® Patient Monitoring and Connectivity Platform, a powerful, expandable hub that integrates an array of technologies, devices, and systems to provide multimodal monitoring and connectivity solutions. Root’s plug-and-play expansion capabilities allow clinicians to simultaneously monitor with O3, SedLine, and other measurements, such as SET® Measure-through Motion and Low Perfusion™ pulse oximetry, providing clinicians with expanded visibility of oxygenation status. Additional modalities available on Root include advanced rainbow® noninvasive measurements such as total hemoglobin (SpHb®) and PVi® (an indicator of fluid responsiveness), NomoLine® capnography, and more – all via an easy-to-interpret, customizable display. Using Root in combination with Masimo Iris Gateway®, monitoring data from O3 can be automatically charted in electronic medical records (EMRs).
Joe Kiani, Founder and CEO of Masimo, said, “O3’s expanded indication as a monitor of the oxygenation and deoxygenation components of cerebral tissue, along with the oxygen saturation of somatic tissue, represents an important milestone in helping clinicians and researchers shed additional light on how the body utilizes oxygen and in uncovering organ hypoxemia.”
@MasimoInnovates | #Masimo
*ARMS accuracy is a statistical calculation of the difference between device measurements and reference measurements. Approximately two-thirds of the device measurements fell within ± ARMS of the reference measurements in a controlled study.
About Masimo
Masimo (NASDAQ: MASI) is a global medical technology company that develops and produces a wide array of industry-leading monitoring technologies, including innovative measurements, sensors, patient monitors, and automation and connectivity solutions. Our mission is to improve patient outcomes and reduce the cost of care. Masimo SET® Measure-through Motion and Low Perfusion™ pulse oximetry, introduced in 1995, has been shown in over 100 independent and objective studies to outperform other pulse oximetry technologies.4 Masimo SET® has also been shown to help clinicians reduce severe retinopathy of prematurity in neonates,5 improve CCHD screening in newborns,6 and, when used for continuous monitoring with Masimo Patient SafetyNet™ in post-surgical wards, reduce rapid response team activations, ICU transfers, and costs.7-10 Masimo SET® is estimated to be used on more than 200 million patients in leading hospitals and other healthcare settings around the world,11 and is the primary pulse oximetry at 9 of the top 10 hospitals according to the 2020-21 U.S. News and World Report Best Hospitals Honor Roll.12 Masimo continues to refine SET® and in 2018, announced that SpO2 accuracy on RD SET® sensors during conditions of motion has been significantly improved, providing clinicians with even greater confidence that the SpO2 values they rely on accurately reflect a patient’s physiological status. In 2005, Masimo introduced rainbow® Pulse CO-Oximetry technology, allowing noninvasive and continuous monitoring of blood constituents that previously could only be measured invasively, including total hemoglobin (SpHb®), oxygen content (SpOC™), carboxyhemoglobin (SpCO®), methemoglobin (SpMet®), Pleth Variability Index (PVi®), RPVi™ (rainbow® PVi), and Oxygen Reserve Index (ORi™). In 2013, Masimo introduced the Root® Patient Monitoring and Connectivity Platform, built from the ground up to be as flexible and expandable as possible to facilitate the addition of other Masimo and third-party monitoring technologies; key Masimo additions include Next Generation SedLine® Brain Function Monitoring, O3® Regional Oximetry, and ISA™ Capnography with NomoLine® sampling lines. Masimo’s family of continuous and spot-check monitoring Pulse CO-Oximeters® includes devices designed for use in a variety of clinical and non-clinical scenarios, including tetherless, wearable technology, such as Radius-7® and Radius PPG™, portable devices like Rad-67™, fingertip pulse oximeters like MightySat® Rx, and devices available for use both in the hospital and at home, such as Rad-97®. Masimo hospital automation and connectivity solutions are centered around the Masimo Hospital Automation™ platform, and include Iris Gateway®, Patient SafetyNet, Replica™, Halo ION™, UniView™, UniView: 60™, and Masimo SafetyNet™. Additional information about Masimo and its products may be found at www.masimo.com. Published clinical studies on Masimo products can be found at www.masimo.com/evidence/featured-studies/feature/.
ORi and RPVi have not received FDA 510(k) clearance and are not available for sale in the United States. The use of the trademark Patient SafetyNet is under license from University HealthSystem Consortium.
References
- Hoffman et al. Perioperative perfusion assessed by somatic NIRS predicts postoperative renal dysfunction. Anesthesiology 2005; 103: A1327*.
- Lecluyse et al. Desaturation in the Intensive Care Unit: Preliminary Experience and Review. J Cardiothoracic Vascular Anesth. (2017) 1805-1809.
- Denault A et al. A Practical Approach to Cerebro-Somatic Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Whole-Body Ultrasound. J Cardio Vasc Anesth. 2019;03.039. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jvca.2019.03.039
- Published clinical studies on pulse oximetry and the benefits of Masimo SET® can be found on our website at http://www.masimo.com. Comparative studies include independent and objective studies which are comprised of abstracts presented at scientific meetings and peer-reviewed journal articles.
- Castillo A et al. Prevention of Retinopathy of Prematurity in Preterm Infants through Changes in Clinical Practice and SpO2 Technology. Acta Paediatr. 2011 Feb;100(2):188-92.
- de-Wahl Granelli A et al. Impact of pulse oximetry screening on the detection of duct dependent congenital heart disease: a Swedish prospective screening study in 39,821 newborns. BMJ. 2009;Jan 8;338.
- Taenzer A et al. Impact of pulse oximetry surveillance on rescue events and intensive care unit transfers: a before-and-after concurrence study. Anesthesiology. 2010:112(2):282-287.
- Taenzer A et al. Postoperative Monitoring – The Dartmouth Experience. Anesthesia Patient Safety Foundation Newsletter. Spring-Summer 2012.
- McGrath S et al. Surveillance Monitoring Management for General Care Units: Strategy, Design, and Implementation. The Joint Commission Journal on Quality and Patient Safety. 2016 Jul;42(7):293-302.
- McGrath S et al. Inpatient Respiratory Arrest Associated With Sedative and Analgesic Medications: Impact of Continuous Monitoring on Patient Mortality and Severe Morbidity. J Patient Saf. 2020 14 Mar. DOI: 10.1097/PTS.0000000000000696.
- Estimate: Masimo data on file.
- http://health.usnews.com/health-care/best-hospitals/articles/best-hospitals-honor-roll-and-overview.
Forward-Looking Statements
This press release includes forward-looking statements as defined in Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933 and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, in connection with the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These forward-looking statements include, among others, statements regarding the potential effectiveness of Masimo O3®. These forward-looking statements are based on current expectations about future events affecting us and are subject to risks and uncertainties, all of which are difficult to predict and many of which are beyond our control and could cause our actual results to differ materially and adversely from those expressed in our forward-looking statements as a result of various risk factors, including, but not limited to: risks related to our assumptions regarding the repeatability of clinical results; risks related to our belief that Masimo's unique noninvasive measurement technologies, including Masimo O3, contribute to positive clinical outcomes and patient safety; risks related to our belief that Masimo noninvasive medical breakthroughs provide cost-effective solutions and unique advantages; risks related to COVID-19; as well as other factors discussed in the "Risk Factors" section of our most recent reports filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission ("SEC"), which may be obtained for free at the SEC's website at www.sec.gov. Although we believe that the expectations reflected in our forward-looking statements are reasonable, we do not know whether our expectations will prove correct. All forward-looking statements included in this press release are expressly qualified in their entirety by the foregoing cautionary statements. You are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements, which speak only as of today's date. We do not undertake any obligation to update, amend or clarify these statements or the "Risk Factors" contained in our most recent reports filed with the SEC, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as may be required under the applicable securities laws.
View source version on businesswire.com: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20200831005390/en/
Source: Masimo