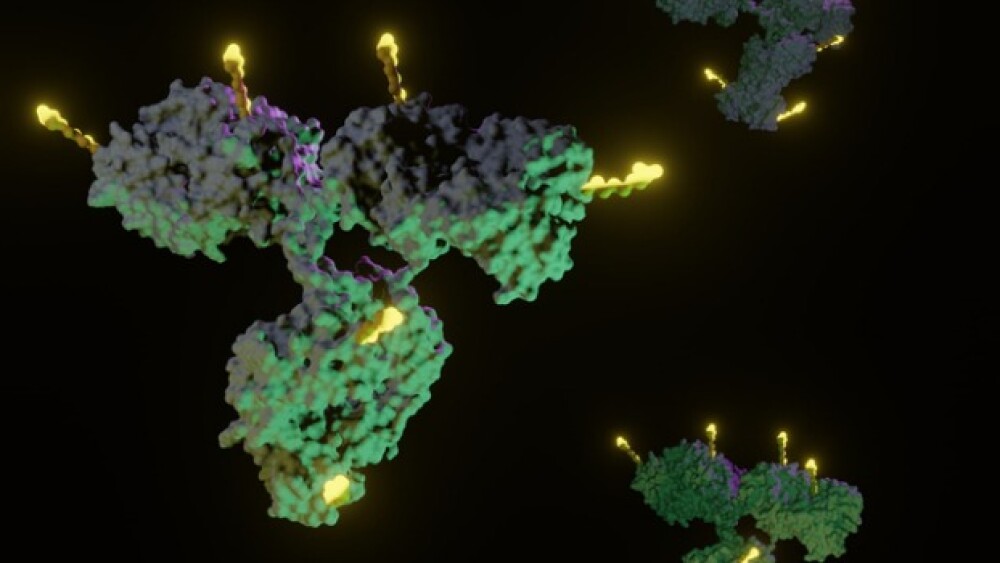
In a finding that could have profound implications for AIDS vaccine design, researchers led by a team at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), have generated an atomic-level picture of a key portion of an HIV surface protein as it looks when bound to an infection-fighting antibody. Unlike much of the constantly mutating virus, this protein component is stable and — more importantly, say the researchers — appears vulnerable to attack from this specific antibody, known as b12, that can broadly neutralize HIV.>>> Discuss This Story