Recce Pharmaceuticals Ltd (ASX:RCE) (FSE:R9Q) (Company), the Company developing new classes of synthetic anti-infectives, is pleased to announce positive results from a pre-clinical study investigating the Mechanism of Action (MoA) of its lead compound RECCE® 327 (R327).
SYDNEY, Australia, June 01, 2021 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Recce Pharmaceuticals Ltd (ASX:RCE) (FSE:R9Q) (Company), the Company developing new classes of synthetic anti-infectives, is pleased to announce positive results from a pre-clinical study investigating the Mechanism of Action (MoA) of its lead compound RECCE® 327 (R327). R327 is a broad-spectrum synthetic anti-infective that has potential to address the urgent global health threat posed by antibiotic resistant superbugs and emerging viral pathogens.
“The data from this study further supports the potential of RECCE® 327 to provide a novel and universal way to treat harmful infections,” said Executive Director & Chief Scientific Officer Michele Dilizia. “We are excited about these highly encouraging results as they provide important insights regarding how RECCE® 327 is able to work repeatedly against the same strain of bacteria and their superbug forms.
The study was performed by independent, world leaders in bacterial Mechanism of Action analysis and antibiotic profiling.
Keytakeawaysfromthis studyare asfollows:
- R327rapidlyandirreversiblyshutsdowncellarenergetics (adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production) – primary MoA
- R327 affects the assembly of bacterial cell division complex, components that require cellular energy to remain assembled, confirming its ability to disrupt cellular bioenergetics
- R327 results in the decreased formation of the bacterial cell division complex into ring-like structures (Z-rings) in a concentration dependent manner
- R327doesnotpermeabilizethecellmembraneoraltertheintegrityoftheoutermembrane of E.coli cells – intended activity without toxicity
- At higher concentrations andsubsequenttoATPshutdown,celllysis(bacterialburstingduetotheiruniquelyhigh internalpressures)can occurasafurthermechanismofaction
- R327rapidlyandirreversiblybactericidaltoslow-growing, quiescent or stationary phase E.coli cells in addition to actively dividing E.coli cells
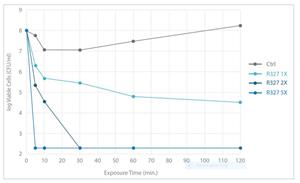
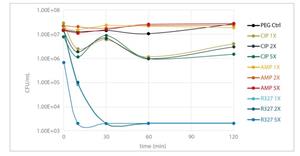
- Within a minute, the highest concentration of R327 used, 5x minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), was observed to reduce viable cell counts reported as cell forming units per milliliter of culture (CFU/ml) 100-fold (>1x107 to 1x105 at timepoint 0)
- Current antibiotics rarely retain bactericidal activities against nondividing or stationary-phasebacterialcells; however, R327 showed remarkableactivityagainstslow-growingbacteriatherebyindicatingpotentialantibacterialactivityin biofilms
- In comparison to ampicillin and ciprofloxacin, R327isabletooutperformbothoftheseantibiotics in bactericidal activity (as measured by viable cell counts) against stationary cells
Study1–DeterminationofMinimumInhibitory Concentration
Initial studies were undertaken to determine the MIC of R327 against various test strains of Gram-negative Escherichiacoli (E.coli) bacteria in their actively growing (dividing) form to ultimately elucidate R327’s MoA. All conditions started with 1x108 CFU/ml E. coli cells which were then treated with R327 for the indicated period of time.
A graphic accompanying this announcement is available at https://www.globenewswire.com/NewsRoom/AttachmentNg/5d6da13a-49b3-4714-b7d3-98a82f772a59
The bactericidal effect was evident immediately in all tested concentrations. In 5x MIC of R327 ‘crashing’ the ATP viability of bacterial cells in minutes, reportedly faster than any antibiotic tested previously.
Study 2 –EfficacyofR327againstactivelygrowing ordividingE. coli
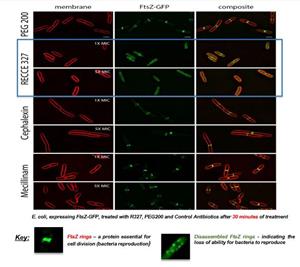
Second study determined whether R327 affects the assembly of the bacterial cell division complex. Cell division in bacteria is mediated by the tubulin-like protein FtsZ – a protein essential for cell division (bacteria reproduction) that requires cellular energy.
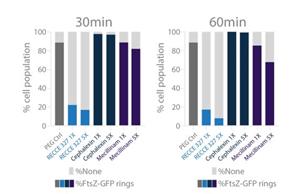
The E. coli clinical isolates were treated to 1x and 5x MIC for 30 minutes and showed 22% (1x MIC) and 17% (5x MIC) of the cells contained FtsZ rings, with the remaining cells containing small FtsZ-GFP filaments, suggesting mid-cellFtsZ ringshaddisassembled.
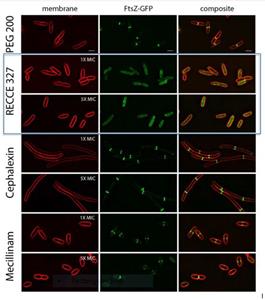
By 60 minutes, only 17% (1x MIC) and 8% (5x MIC) contained FtsZ rings. The remaining cells displayed small amount of FtsZ-GFPandwascompletelydiffusedthroughoutthecell, indicating a disassembledFtsZ-GFP.
These results highlight a decreased occurrence of FtsZ-GFP rings in a concentration dependent manner, concluding that treatment with R327 leads to disassembly of the FtsZ-GFP rings (notallowingbacterialcellstodivide,multiply andspreadinfection).
A graphic accompanying this announcement is available at https://www.globenewswire.com/NewsRoom/AttachmentNg/d5dc4e52-a1eb-46e9-b9cc-d070f5801f2f
The image shows treatment of R327 against E. coli at 1x and 5x MIC leading to disassembly of the FtsZ-GFP rings, supporting initial studies which indicated R327 inactivates cellular bioenergetics and is rapidly and irreversibly bactericidal.
Graphics accompanying this announcement are available at:
https://www.globenewswire.com/NewsRoom/AttachmentNg/c9744ffa-84cb-4739-9add-3a2d07a0956e
https://www.globenewswire.com/NewsRoom/AttachmentNg/6bad6567-14fa-4944-b185-bf8f56dc50c3
Study 3 –EfficacyofR327againstnondividingorstationary-phaseE. coli
A separate, but related study undertaken was to determine whether R327 is active against nondividing or stationary-phase E.coli using clinical isolate cells.
A graphic accompanying this announcement is available at https://www.globenewswire.com/NewsRoom/AttachmentNg/68a57e67-3013-419c-9121-e5d738a59092
Currentantibioticsrarelyretainbactericidalactivitiesagainstnondividingbacterialcells;however,R327 shows significantactivity againstboth slow-growing bacteria and activelydividingcells,therebyenablingcontinuoustreatmentofinfectionsthroughoutthebacterialcelllifecycle.
After only 10 minutes of R327 at 1x and 2x MIC, the viable cell counts decreased 100-fold, and after another 30 minutes, cell count decreased further to 10,000-fold (approximately). When exposed to the highest concentration, 5x MIC of R327, viable cell counts decreased 10,000-fold within 10 minutes. In comparison to the positive and negative controls, the report found ampicillin to be nearly completely resistant and ciprofloxacin only having mild activity against the cells.
These findings are aimed at elucidating R327’s mechanism of action and will be presented at the World Microbe Forum taking place virtually 20-24 June 2021. Similarly, studies are underway to explore the effect and MoA of R327 on Gram-positive bacteria.
AboutReccePharmaceuticalsLtd
Recce Pharmaceuticals Ltd (ASX: RCE) is pioneering the development and commercialization of New Classes of Synthetic Anti-Infectives designed to address the urgent global health problems of antibiotic resistant superbugs and emerging viral pathogens.
Recce’s anti-infective pipeline is unique and comprised of broad-spectrum synthetic polymer antibiotics RECCE® 327, RECCE® 435, and RECCE® 529 for viral infections with unique mechanisms of action against hyper-mutation on bacteria and viruses, respectively.
Patented lead candidate RECCE® 327 has been developed for the treatment of blood infections and sepsis derived from E. coli and S. aureus bacteria – including their superbug forms. Recce’s new antibiotic compound, RECCE® 435, has been formulated for oral use.
The FDA has awarded RECCE® 327 QualifiedInfectiousDiseaseProduct designation under the GeneratingAntibiotic Initiatives Now (GAIN) Act – labelling it for Fast Track Designation, plus 10 years of market exclusivity post approval. Further to this designation, RECCE® 327 has been included on The Pew Charitable Trusts Global New Antibiotics in Development Pipeline as the only synthetic polymer and sepsis drug candidate in development.
Recce wholly owns its automated manufacturing, ready to support first-in-human clinical trials. Recce’s anti- infective pipeline seeks to exploit the unique capabilities of RECCE® technologies targeting synergistic, unmet medical needs.
Corporate Contact
James Graham
Recce Pharmaceuticals Ltd
+61 (02) 8075 4585
James.graham@recce.com.au
Media and Investor Relations (AU)
Andrew Geddes
CityPR
+61 (02) 9267 4511
ageddes@citypublicrelations.com.au
Media and Investor Relations (USA)
Jordyn Temperato
LifeSci Communications
jtemperato@lifescicomms.com
Determination of minimum inhibitory concentration
Viable Cell Counts for E. coli ATCC 25922 treated with B0063 for the indicated time before washout, initial inoculum of ~108 CFU/ml.
Impact of R327 on E. coli cell membranes after 30 minutes of treatment
E. coli, expressing FtsZ-GFP, treated with R327, PEG200 and Control Antibiotics after 30 minutes of treatment
Impact of R327 on E. coli cell membranes after 60 minutes of treatment
E. coli, expressing FtsZ-GFP, treated with R327, PEG200 and Control Antibiotics after 60 minutes of treatment
Quantification of FtsZ-GFP rings in E. coli treated with R327 at various timepoints
Quantification of FtsZ-GFP rings in E. coli treated with R327 andother control antibiotics Cephalexin and Mecillinam at 30 minutes and/or 60 minutes
Efficacy of R327 against nondividing or stationary-phase E. coli