Phase 1
Over the past year, obesity treatments have become the focus of intense media attention and discussion in healthcare — with increased focus on Wegovy and Zepbound. This attention has highlighted the need to address the global obesity epidemic.
Patients treated with Longboard Pharmaceuticals’ bexicaserin saw a 32.5% drop in the frequency of countable motor seizures relative to placebo in a Phase 1b/IIa study. The company’s shares soared 316% Tuesday on the news.
Gene therapy company uniQure announced Tuesday “ongoing evidence” of a clinical benefit for its Huntington’s disease treatment. However, investors were not impressed as the stock dropped nearly 20%.
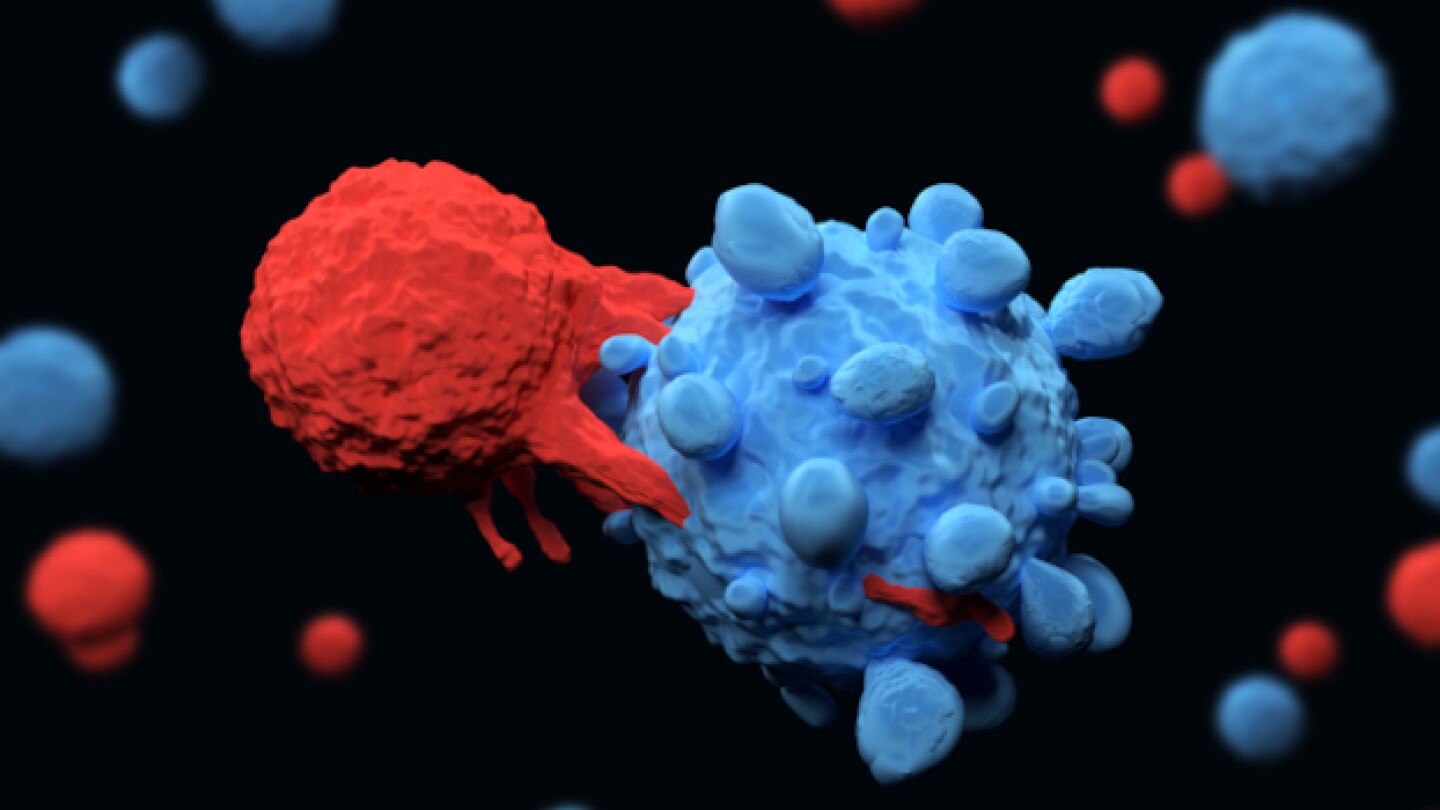
The investigational allogeneic CAR-T therapy P-BCMA-ALLO1 appears to be more effective following strong immunosuppressive preconditioning.
From the skin to the lungs to the central nervous system, biotech companies are making progress toward delivering RNA therapeutics to multiple targets throughout the body. But challenges remain.
This week, the FDA could approve the first CRISPR-edited therapy in the U.S., while two other companies await decisions on topical drugs.
Advancements in asthma biologics spell future hope for patients with severe asthma.
As companies clamor for a piece of the antibody-drug conjugate pie, experts pose the question: is it possible to replicate the success of Enhertu?
BioSpace takes a deep dive into five investigational therapeutic cancer vaccines that have recently shown efficacy in difficult-to-treat indications.
The Japanese pharma contends that an analysis of the four deaths in its AT132 gene therapy clinical trial shows it is still viable as a potential treatment for a fatal, rare genetic disease.
PRESS RELEASES